SISCO's excellent and advanced manufacturing process ensures that the fire monitoring residual current transformer meets the technical requirements for accuracy level and reliability, complying with the standards GB-14287.2-2005 and GB-14287.2-2014. This guarantees the product's stable performance and long-term operational safety in demanding applications.
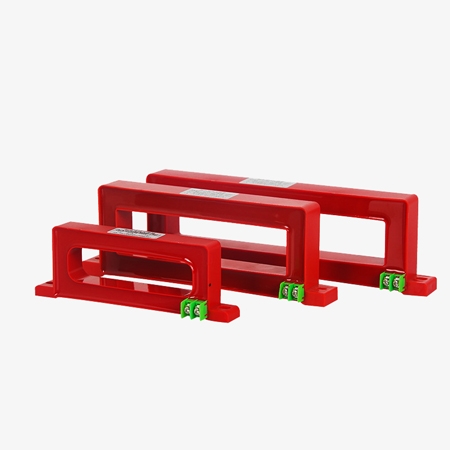

Exceptional Core Performance and Enhanced Stability
- Core-through structure with flame-retardant epoxy resin casting ensures excellent stability.
- Made with high-permeability nickel steel or nanocrystals for superior linearity and high sensitivity.
- Open/closed design with a unique structure for residual current transformer easy installation and debugging.

Advanced Material Selection and User-Friendly Installation
- Premium ABS housing with high impact strength, non-toxic, and odorless.
- Outstanding balance characteristics and strong resistance to electromagnetic interference.
- Stainless steel clamps for durability and reliability of zero-sequence residual current transformer.
Applications
The zero-sequence residual current transformer is widely used in various critical applications, including electrical fire monitoring, fire leakage protection systems, smart electricity systems, low-current grounding systems, electromagnetic relay protection, and microprocessor-based protection systems. It plays a vital role in ensuring electrical safety by detecting leakage currents and preventing electrical fires. Additionally, it is crucial in systems that require precise monitoring of electrical conditions, such as power distribution networks, industrial control systems, and renewable energy installations. Its reliable performance contributes to the protection of both equipment and human safety in complex electrical environments.

Fire Leakage Protection

Smart Electricity Systems

EM Relay Protection

Electrical Fire Monitoring
| Model | SISCO-RCT-F1025 |
| Rated Output | 10MA-1A |
| Operating Frequency | 50~400Hz |
| Operating Temperature | -12℃~+45°C |
| Humidity | ≤85% |
| Installation | Closed/Open selectable |
| Shell | ABS, flame retardant grade 94-V0 |
| Internal Structure | Environmentally friendly epoxy resin |
| Wiring Method | Terminal type/shielded stranded wire 1.5m |
| Weight | ±1.5kg |
Details
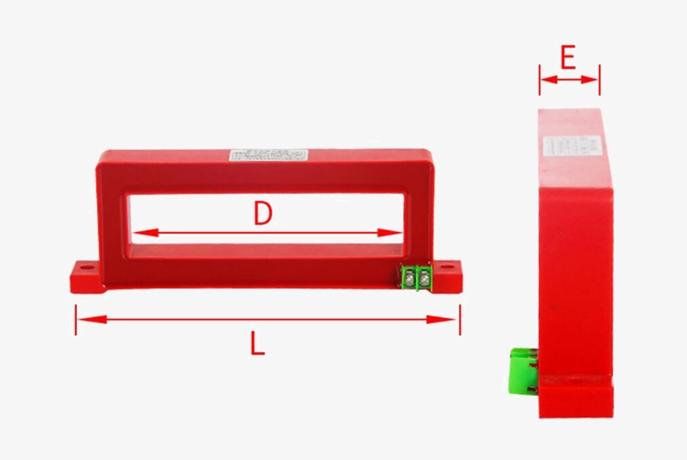
| Model | D | E | L | Phase Current |
| RCT-F1025 | Φ100*25 | 19 | 155 | 0-100A |
| RCT-F1435 | Φ140*35 | 24 | 203 | 0-250A |
| RCT-F1835 | Φ180*35 | 24 | 246 | 0-400A |
| RCT-F2247 | Φ220*47 | 24 | 280 | 0-630A |
| RCT-F2647 | Φ260*47 | 24 | 326 | 0-800A |
| RCT-F3047 | Φ300*47 | 24 | 366 | 0-1250A |
| RCT-F3647 | Φ360*47 | 24 | / | 0-2000A |
| RCT-F4247 | Φ420*47 | 24 | / | 0-2500A |
Q1: What causes leakage current?
A1: Leakage current is typically caused by faults in the insulation of electrical wiring or equipment, allowing current to flow through unintended paths, such as the ground or through moisture. Common causes include damaged cables, aging or degraded insulation, faulty electrical appliances, or environmental factors like humidity, water, or corrosive materials that can compromise the integrity of the electrical system. Additionally, improper installation or grounding issues can also lead to leakage currents, posing a safety risk of electric shock or fire.
Q2: What is the difference between an RCT and a CT (Current Transformer)?
A2: The key difference between an RCT (Residual Current Transformer) and a CT (Current Transformer) lies in their function and purpose. An RCT is designed to detect the imbalance or difference between the live (phase) and neutral currents in a circuit, indicating the presence of leakage current, which is crucial for safety and protection against electric shocks or fires. In contrast, a CT is used to measure the total current flowing through a conductor, typically for monitoring, metering, or protection purposes in normal operating conditions. While a CT provides information on the magnitude of current in a circuit, an RCT focuses on detecting any current leakage or residual current, which can signal a fault or safety issue.
Q3: What is the typical current rating of an residual current transformer?
A3: The typical current rating of a Residual Current Transformer (RCT) varies depending on the application and the level of sensitivity required. For residential and commercial use, RCTs are commonly rated for leakage currents of 30 mA, which is considered sufficient for protecting against electric shock hazards. In industrial settings, where higher currents and more robust protection are needed, RCTs may be rated for leakage currents of 100 mA, 300 mA, or even higher. The current rating is designed to detect imbalances between the phase and neutral currents, and the sensitivity of the RCT is chosen based on the level of protection required in the specific installation.
Tips: How does a residual current transformer work?
An RCT (Residual Current Transformer) works by monitoring the difference in current between the live (phase) and neutral conductors in an electrical circuit. Under normal conditions, the current flowing through the live and neutral wires is equal and balanced. However, if there is a leakage current, such as when electricity escapes to the ground through a fault or damaged insulation, the balance is disturbed. The RCT detects this imbalance and generates a signal, which triggers a protective device, such as a Residual Current Device (RCD), to disconnect the circuit and prevent potential electric shocks or fires. The RCT is typically installed around the live and neutral wires of the circuit, enabling it to measure the residual current flowing through the system.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

