A water activity meter is a device used to measure the water activity (aw) of a substance, which indicates the availability of water for microbial growth and chemical reactions in that substance. Water activity refers to the ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a sample to the vapor pressure of pure water under the same conditions. This article SISCO will introduce the principle of water activity meter in detail from the aspects of water adsorption, infrared drying method, chemical method, vapor pressure method, refractive index method, coulometric method, thermogravimetric method, Raman spectroscopy, etc.
Moisture Adsorption
Water adsorption is one of the basic principles of water activity meters. The water activity meter obtains the water activity of the sample by measuring the vapor pressure of water molecules in the sample or the relative humidity at the adsorption /desorption equilibrium. At a certain temperature, the amount of water adsorbed by a substance is proportional to the vapor pressure. Therefore, by measuring the vapor pressure or relative humidity, the water activity of the sample can be calculated.
Infrared Drying Method
The infrared drying method uses infrared radiation to evaporate the water in the sample, and at the same time measures the change in the sample weight to calculate the water content in the sample. The water activity meter uses a high-precision weighing sensor and an infrared drying device to evaporate the water in the sample in a short time and accurately measure the weight change of the sample. By measuring the weight change of the sample and the weight after drying, the water activity of the sample can be calculated.
Chemical Method
The chemical method is to convert the water in the sample into hydrogen ions or other ions through chemical reactions, and then determine the water content through ion chromatography or other chemical analysis methods. Commonly used chemical methods include Karl Fischer method, anhydrous sodium carbonate method and toluene method. The water activity meter uses the principle of Karl Fischer method to measure the amount of reagent consumed at the titration endpoint by reacting the titration reagent with the water in the sample, thereby calculating the water activity of the sample.
Steam Pressure Method
The vapor pressure method determines the water activity of a sample by measuring the saturated vapor pressure or dew point temperature. When the relative humidity of the sample reaches 100%, the water molecules will change from the liquid phase to the gas phase, generating saturated vapor pressure. The vapor pressure of the sample is related to temperature and humidity, so by measuring the vapor pressure or dew point temperature of the sample, the water activity of the sample can be calculated .
Refractive Index Method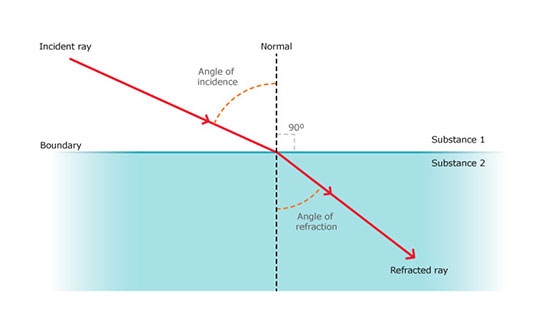
The refractive index method determines the water content in a sample by measuring the refractive index of the sample. Water molecules are polar and can interact with other polar molecules, thus affecting the refractive index of the sample. The water activity meter uses the principle of optical interference to measure the refractive index of the sample and calculates the water activity of the sample based on the pre-determined relationship between the refractive index and the water activity.
Coulometric Method
the charge properties of water molecules in an electric field . Water molecules have polarity and can be oriented in an electric field to generate an induced dipole moment. The water activity meter uses capacitance or impedance measurement methods to measure the change in the charge of the sample in an electric field, and calculates the water activity of the sample based on the relationship between the pre-measured charge and water activity.
Thermogravimetry
Thermogravimetry is a method of determining the water content of a sample by measuring the mass change of the sample during heating. Water molecules will gradually evaporate during heating, causing the mass of the sample to gradually decrease. The water activity meter uses a high-precision balance to measure the mass change of the sample and calculates the water activity of the sample based on the relationship between the mass change and the water activity measured in advance.
Raman Spectroscopy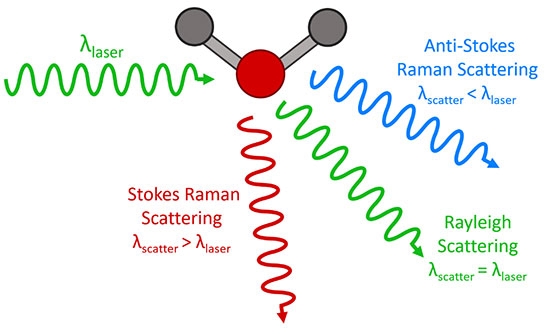
Raman spectroscopy is a method of measuring the water content of a sample by measuring the Raman scattering spectrum of the sample. Raman scattering is a phenomenon in which light is scattered when it propagates in a substance. The intensity of the scattered light is related to the molecular vibration energy level of the substance. The water activity meter uses a fiber optic probe and a spectral analysis system to measure the Raman scattering spectrum of the sample and calculate the water activity of the sample based on the relationship between the Raman spectrum and the water activity that has been measured in advance.
In summary, the principle of AW meter is mainly based on water adsorption, infrared drying method, chemical method, vapor pressure method, refractive index method, coulometric method, thermogravimetric method and Raman spectroscopy. These methods respectively determine the water activity in the sample through different physical and chemical principles, providing accurate water analysis methods for various industries.

