The manual three-jaw chuck concentricity tester offers a precise solution for measuring concentricity, especially for threaded workpieces. With a 360° rotating stand for easy positioning and hand-crank operation, the tester is both user-friendly and efficient. Simply lift the angle positioning pin, rotate clockwise, and turn the handwheel to easily conduct measurements, making it versatile for various measurement scenarios, from small workshops to large manufacturing facilities.
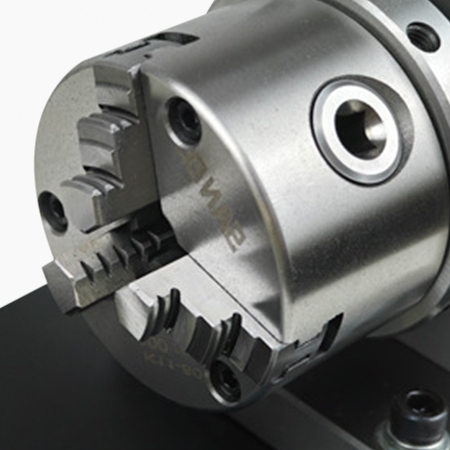

Functional Concentricity Gauge
- Three-jaw fixed measurement, more precise, can clamp workpieces with threads.
- The tester can be used in various measurement scenarios.
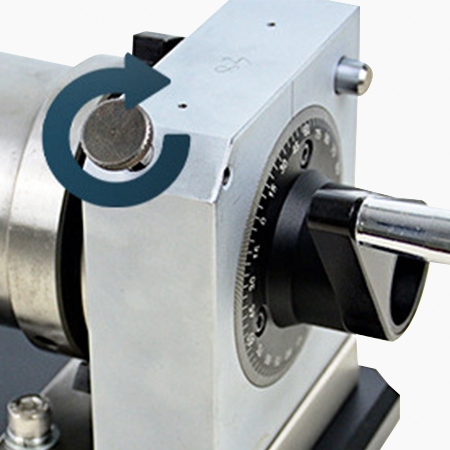

Easy Operation of Concentricity Measurement
- The stand can rotate 360°, making the measurement operation easier.
- Hand-crank operation, simpler to use. Lift the angle positioning pin, rotate clockwise, and turn the handwheel to measure.
Application
The concentricity tester measures the alignment of an object's central axis to ensure concentricity. It is widely used across industries: in aerospace, it verifies the alignment of parts in aircraft engines and spacecraft; in the automotive industry, it ensures precise alignment of components like engines and transmissions; and in electronics, it checks the concentricity of motors and other precision components; in mechanical manufacturing, it checks the concentricity of rotating parts like shafts and bearings. These applications highlight the importance of concentricity for product quality and performance.

Automotive Industry

Electronics

Mechanical Manufacturing

Aerospace
| Model | Accuracy (mm) | Forward Jaw Clamping (mm) | Reverse Jaw Clamping (mm) | Inner Support (mm) | Central Through Hole (mm) |
| Standard Three-Jaw Concentricity Tester | |||||
| SISCO-CT-ACE-80C | 0.02 | 2~22 | 22~70 | 25~70 | 16 |
| SISCO-CT-ACE-100C | 0.02 | 2~30 | 30~80 | 30~90 | 22 |
| SISCO-CT-ACE-160C | 0.02 | 3~55 | 55~145 | 50~160 | 45 |
| High-Precision Three-Jaw Concentricity Tester | |||||
| SISCO-CT-ACE-8063 | 0.005 | 2~22 | 22~70 | 25~70 | 16 |
| SISCO-CT-ACE-1083 | 0.005 | 2~30 | 30~80 | 30~90 | 22 |
| SISCO-CT-ACE-1645 | 0.005 | 3~55 | 55~145 | 50~160 | 45 |
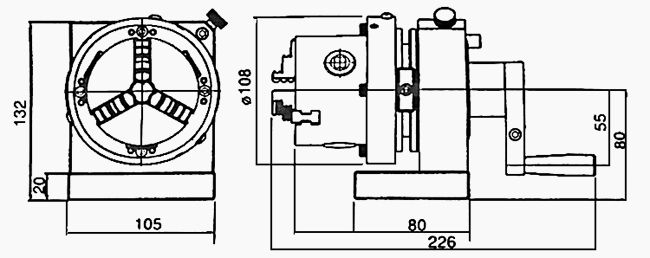
Dimension
Accessories

| Dial Model | Graduation Value | Measuring Range | Dial Reading | Measuring Force |
| 513-404C/0.01 | 0.01 | 0-0.8mm | 0-40-0 | <0.3N |
| 513-405E/0.002 | 0.002 | 0-0.2mm | 0-100-0 | <0.3N |
(Note: The indicator's accuracy should match or be lower than the instrument's accuracy; otherwise, a high-accuracy indicator won't provide practical benefits, and a low-accuracy indicator won't fully utilize the instrument's potential.)
Q1: What is a concentricity tester?
A1: A concentricity tester is a precision measurement tool used to assess the alignment of the centers of two or more parts, ensuring they are concentric (i.e., share the same center axis). This tool is commonly used in machining and manufacturing to check the concentricity of components like shafts, bearings, and other cylindrical parts. By rotating the component and measuring any deviation from the desired axis, the tester provides insight into the part's precision and how well it will function in an assembly. Concentricity gauges are crucial in quality control to minimize mechanical errors, reduce wear and tear, and improve the overall performance of the finished product.
Q2: How does a concentricity tester work?
A2: A concentricity tester works by measuring the alignment between the center axes of a part and its rotating reference. The part being tested, typically a cylindrical component like a shaft, is mounted securely on a spindle or fixture. As the part rotates, one or more dial indicators or measuring probes are placed at key points along the part's surface, often at both ends. These indicators measure any deviation from the ideal concentric position, detecting even small variations in the part's roundness or alignment. The concentricity measuring equipment records the amount of offset or eccentricity, providing a precise measurement of how much the part deviates from being perfectly concentric. This helps ensure high precision in manufacturing, reducing mechanical errors and improving the performance and longevity of the final product.
Q3: How to ensure proper maintenance and care for the concentricity testers?
A3: To ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the concentricity testers, it is important to keep all components clean. If there is fine dust, use a blower balloon to gently remove it, and if there are oil stains or fingerprints, wipe them off with a soft cotton cloth. Do not attempt to disassemble the instrument, as this could compromise its measurement accuracy or cause damage. When not in use, always cover the tester with a dust cover to prevent dust accumulation. Additionally, apply anti-rust oil and store the tester in a dry environment to avoid rusting. To maintain its performance, regular inspections are recommended. If you have any questions during use, please contact customer service for assistance.
Tips: How to choose a proper dial indicator for your concentricity tester?
When selecting a dial indicator for a concentricity measuring equipment, the first factor to consider is accuracy. The dial indicator should have a high resolution to detect even the smallest deviations in concentricity. For precision work, an indicator with a resolution of 0.001 mm or 0.0001 inch is ideal, as it allows for fine adjustments and detailed measurements. The total range or travel of the dial indicator should also be appropriate for the expected variations in the workpiece, ensuring that the indicator can accurately capture the maximum deviation without bottoming out or overextending.
Another important consideration is the type of indicator and its compatibility with the concentricity tester. The most common types are mechanical dial indicators and digital indicators. Mechanical indicators are simpler, cost-effective, and sufficient for many applications, while digital indicators provide higher precision and easy-to-read results. When selecting an indicator, ensure that it fits the mounting setup of the concentricity tester and that the measuring probe is suitable for the workpiece material and surface. Proper indicator selection enhances measurement accuracy, ensuring reliable results for various applications.
In addition to the dial indicators available on this page, there are other dial indicators provided on our SISCO website you can choose from.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

