The 3 phase sequence meter adopts clamp-type induction measurement, which does not require to open the wires to contact the exposed high-voltage live wires, and has double insulation protection, which is safer to operate. The continuous use time of a 9V battery is about 70 hours.
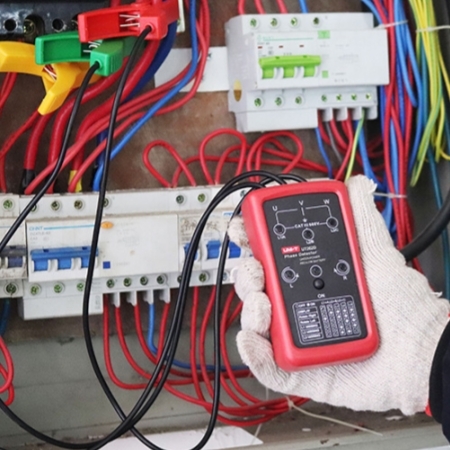

Phase Sequence Detection of Power Distribution Cabinet
- During measurement, if the R indicator light is on and the instrument emits intermittent short beeps, the phase line being clamped is in the positive phase sequence, L1-L2-L3 (i.e. U-V-W).
- If the L indicator light is on and the instrument emits continuous long beeps, the phase line being clamped is in the reverse phase sequence (i.e. W-V-U).
Phase Detection
- Use any clamp to clamp the three-phase line separately. If there is a phase loss, the L1, L2 or L3 lights will not light up.
- Use any clamp to clamp the wire along the line to be repaired. If the L1, L2, or L3 lights at the clamp measurement point are not on, the line before this point is broken. Shortening the position of the clamp measurement point can accurately find the line break position (breakpoint positioning), which is very convenient and safe for line maintenance.
- This function is very suitable for repairing circuit break faults in the line, safely and fast.
Applications
The application scenarios of phase sequence meters are very wide, covering multiple fields from basic power system debugging to complex industrial control systems. It has a wide range of applications in multiple fields. It not only ensures the correct operation of the equipment but also improves the safety and efficiency of the system. With the continuous advancement of technology, the functions of the phase sequence meter will be more diversified in the future, and its application in various fields will become more popular and important.

Equipment Maintenance

Factory Area
Teaching Experience

Electrician Field
| Model | SISCO-PRM-UT262D |
| Power Supply | 9V battery, continuous use time is about 70 hours |
| Measurement Method | Non-contact wire clamping method |
| Wire Location | The wire to be measured is in the center of the jaws |
| Frequency | 50Hz/60Hz automatic recognition |
| Live Power Range | AC 70~1000V, 45Hz/65Hz (sine wave continuous input), static electricity detection. |
| Max. Voltage | AC 1000V |
| Clampable Wire Size | Outside diameter ∅1.5mm~ ∅48mm |
| Buzzers |
[Normal phase] The instrument emits intermittent short beeps. [Reverse phase] The instrument emits continuous long beeps. |
| Supply Indication | Green LED |
| Output Indication | Red LED |
| Clamp Lead Length | 0.6m |
| Automatic Shut-down | About 6 minutes |
| Max. Rated Power | 300mVA |
| Working Temperature and Humidity | -10°C~55°C, under 80% rh |
| Storage Temperature and Humidity | -20°C~60°C, under 90% rh |
| Dielectric Strength | 3.7kVrms |
| Suitable for Safety | EN61010-1: 2001, EN61010-031: 2002 |
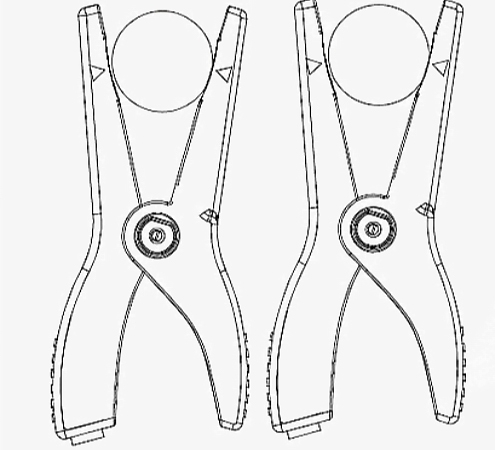
Structure Diagram
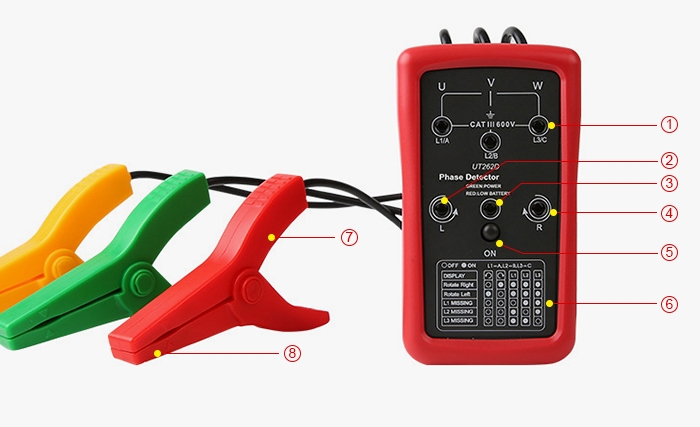

- Test Indicator Light×3
- Power Button
- L Reverse Phase Sequence Indicator Light
- Phase Sequence and Indicator Light Correspondence Table
- Power Indicator Light
- Clamp Handle
- R Positive Phase Sequence Indicator Light
- Clamp Lead Indicator
Q1: What factors can affect the phase rotation meter?
A1: The measurement accuracy and stability of the phase sequence meter may be affected by many factors. First, an unstable power supply or voltage that is too high or too low may cause deviations in the measurement results of the phase sequence meter. Secondly, circuit board aging, component damage, etc. may affect the normal operation of the phase sequence meter. In addition, sensor failure or damage will not be able to correctly detect the phase sequence information of the power supply. Of course, human errors in equipment settings or operating methods can also lead to measurement errors.
Q2: How does a phase rotation meter work?
A2: The working principle of the phase sequence meter is based on the detection and processing of three-phase voltage or current signals. It determines whether the phase sequence is correct by comparing the phase difference between the three-phase voltages. Common phase sequence detection algorithms include those based on zero-sequence detection and those based on positive and negative sequence components. When the phase sequence is correct, these algorithms will output corresponding signals to indicate that the phase sequence is correct; otherwise, they will indicate that the phase sequence is wrong.
Q3: What technical parameters should be paid attention to?
A3: The technical parameters of the phase sequence meter include but are not limited to input voltage range, power supply voltage, meter size, weight, ambient temperature, humidity, etc. These parameters are crucial for evaluating the performance and application scope of the phase sequence meter. In addition, the phase sequence meter must also have a certain insulation strength and anti-interference ability to adapt to different use environments and ensure the safety of operators.
Tips: Maintenance methods of phase sequencer
The maintenance of the phase sequencer should focus on cleaning, checking electrical connections, regular maintenance, and strictly abiding by the instructions for use and maintenance manual. Correct maintenance methods can greatly extend the service life of the phase sequencer and ensure its correct operation in the power system. Safety is always the primary consideration when performing maintenance.
Regular cleaning: Dust and debris on the surface of the phase sequencer should be removed regularly to avoid affecting heat dissipation and service life.
Check electrical connections: Check the terminals regularly to ensure that the plugs and sockets are clean and dry to prevent loose or corroded electrical connections.
Regular inspection and maintenance: This includes checking the components and fault points of the phase sequencer and replacing damaged components in a timely manner.
Storage environment: The phase sequencer should be stored in an environment that avoids moisture, high temperature, and dust.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

