SISCO portable analog multimeter is designed for precision and reliability. Whether you're measuring voltage or resistance, this multimeter provides accurate readings every time.
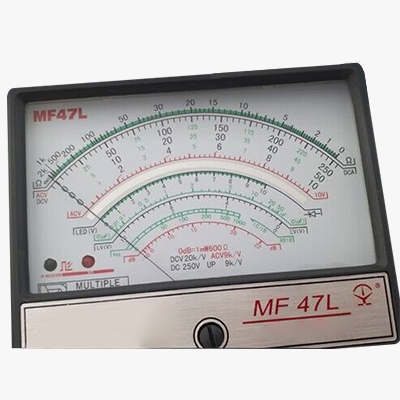

Manual Range Selection
- The portable analog multimeter features an analog multimeter with manual range selection, allowing users to choose the appropriate range for each measurement to ensure accurate readings.
- SISCO pointer multimeter includes a large screen display, making it easy to read measurements clearly and accurately.
- The straightforward design and simple operation make it easy for users to take measurements without complicated setup procedures.
- This pocket analog multimeter is capable of measuring voltage and resistance, providing versatility for various electrical testing needs.

Handheld Design with Rotatable Support Stand
- The portable analog multi meter is designed for handheld use and comes with a rotatable support stand, which can be pulled out or used to prop up the device, facilitating measurements from various angles.
- The handheld design makes it portable and convenient to carry, while the sturdy construction ensures durability for fieldwork or regular use.
- The moving needle display allows for continuous monitoring of fluctuations, providing real-time feedback on the measurements.
- The analog tester's ergonomic design ensures comfortable handling, and the support stand enhances stability during measurements, improving overall user experience.
Applications
SISCO analog multimeter is a versatile tool used in various applications, including electronics repair, electrical maintenance, car repair and laboratory testing. It measures voltage, current, and resistance, and often includes additional features such as capacitance, frequency, and temperature measurement. Its precision and multifunctionality make it essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting electrical issues in both professional and educational settings.

Car Repair
Electronics Repair

Laboratory Testing

Electrical Maintenance
| Model | SISCO-AM-MF47L | ||
| Basic Function | Range | Sensitivity | Accuracy |
| DC Current (DAC) | 0.05mA/0.5mA/5mA/50mA/500mA | 0.25V | ±2.5% |
| 10A | ±5% | ||
| DC Voltage (DCV) | 0.25V/1V/2 .5V/10V/50V | 20kΩ | ±2.5% |
| 250V/1000V | 9kΩ | ||
| 2500V | ±5% | ||
| AC Current (ACV) | 10V/50V/250V/500V/1000V/2500V | ||
| DC Resistance (Ω) | Rx1/Rx10/Rx100/Rx1k/Rx10k | Center value 20 | ±10% |
| Special Function | |||
| Rx100k High Impedance | / | √ | |
| Capacitor (C uF) | Cx1 Cx10 Cx100 Cx1k Cx10k | √ | |
| Channel Buzzer | R<50Ω | √ | |
| Infrared Signal | <±15°, Distance 1~30cm | √ | |
| Audio Level | Rx10hFE, 0-1000 | √ | |
| Transistor (hFE) | / | √ | |
| LV/LI | / | √ | |
| Standard Resistance | / | √ | |
| LED, Zener Diode | / | √ | |
| Self-recovery Protection | / | √ | |
| Dimension | |||
| Battery Specifications | 2X1.5V 2#,1x9V | ||
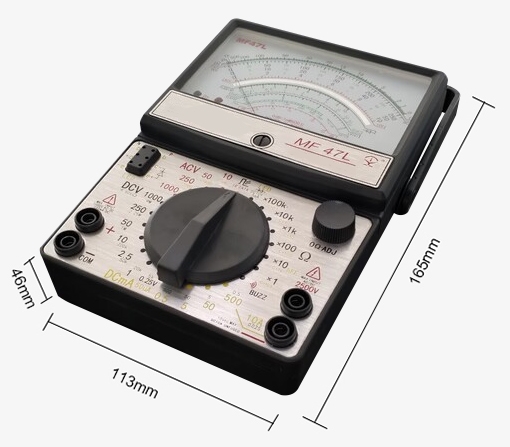
| Analog Multimeter Dimension | 165x116x46mm | ||
| Color Box Dimension | 375x210x54mm | ||
| Net Weight | 800g | ||
Dimension

Details

Q1: What is an analog multimeter?
A1: An analog multimeter is a type of electrical measuring instrument that displays readings via a moving needle over a graduated scale. It is used to measure various electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and resistance in circuits, and it operates on the principle of a moving coil galvanometer.
Compared to digital multimeters, analog multimeters are valued for their ability to show continuous variations in readings, making them particularly useful for observing fluctuations in measurements. However, they are generally considered less accurate and harder to read due to the parallax error and the need for manual range selection.
Q2: How do I zero the analog multimeter for resistance measurements?
A2: To zero an analog multimeter for resistance measurements, first set the multimeter to the lowest resistance range. Touch the two probes together to create a short circuit. Adjust the zero-ohm calibration dial, usually located near the dial or on the side of the meter, until the needle points to zero on the resistance scale. This ensures accurate readings by accounting for any internal resistance in the probes and meter.
Q3: What should I do if the needle doesn't move when taking a measurement?
A3: If the needle doesn't move, check the following:
- Connections: Ensure the probes are securely connected to the multimeter and making good contact with the test points.
- Range Setting: Verify that the range setting is appropriate for the expected measurement. If the range is too high, the needle might not deflect enough to be noticeable.
- Multimeter Functionality: Test the multimeter with a known voltage or resistance to confirm it is functioning correctly. If it still doesn’t move, the meter or the probes may be faulty and need repair or replacement.
Tips: How do you use an analog multimeter for dummies?
Using an analog multimeter is straightforward. Here's a simple guide:
1. Turn the Multimeter On: Locate the power switch and turn the device on.
2. Select the Function: Choose what you want to measure (voltage, current, or resistance). Turn the dial to the appropriate setting (V for voltage, A for current, Ω for resistance).
3. Set the Range: Select the correct range for your measurement. Start with the highest range if you're unsure, then adjust down as needed.
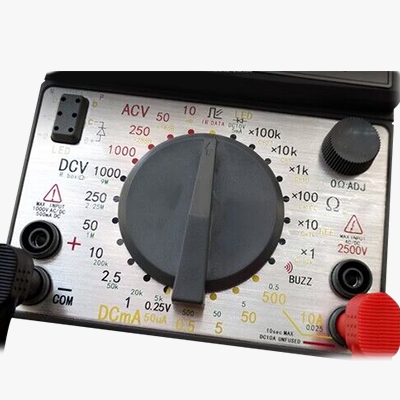
4. Connect the Probes:
- Insert the black probe into the COM (common) socket.
- Insert the red probe into the socket marked VΩmA for most measurements. For high current
measurements, use the 10A socket if available.
5. Take the Measurement:
- Voltage: Place the probes across the component or circuit (red probe to positive, black to negative).
- Current: Break the circuit and connect the probes in series where the current should flow through the meter.
- Resistance: Ensure the circuit is de-energized (no power). Place the probes across the component.
6. Read the Scale: Observe the needle position on the scale. Each scale corresponds to the setting and range you've chosen.
7. Turn Off the Analog Multimeter: After measurement, turn off the device to save battery life.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

