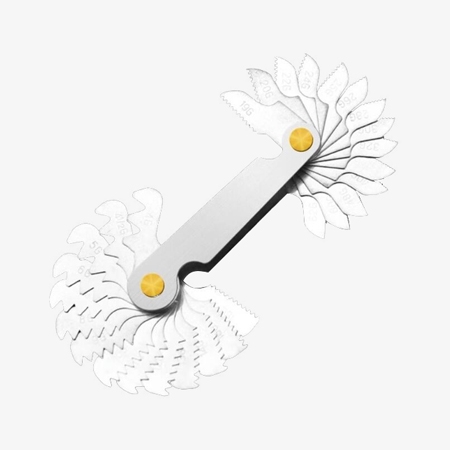
The thread pitch gauge set, compatible with metric, BSP, and US standards, serves as a versatile tool for measuring the threads per inch or centimeter on screws, bolts, or tapped holes. It is an essential tool for any toolbox.
Structural Design and Material Durability
- Detachable design for repeated use, convenient for disassembly and storage, making the thread pitch gauge practical for frequent tasks.
- Made of high-quality stainless steel, elastic, rust-resistant, and not easily breakable, durable material that withstands daily wear and harsh environments.

Precision Measurement and Performance Features
- Single blade thickness: 0.65mm, ensures precise cutting and accurate measurements.
- Stamping process with clear, scratch-resistant markings, providing reliable readings even after long-term use.
- Complete range of metric, British, and American specifications to meet all your needs, which is suitable for a wide range of applications and standards.
Applications
Metric, imperial, and US thread pitch gauges are widely used across various industries for precise measurement and verification of thread pitches. In machining and manufacturing, they ensure that threaded parts conform to exact specifications for optimal fit and function. For thread identification, these gauges quickly determine thread types and sizes, reducing errors during assembly or repairs. In tool and die making, they help verify dimensions during production, maintaining accuracy in creating threaded components. The aerospace and automotive industries rely on these gauges to ensure compliance with rigorous thread standards, vital for safety and performance in critical applications.

Thread Identification

Tool and Die Making

Automotive Industries

Machine Manufacturing
| Genral Characteristics | |||||||
| Model | SISCO-TG-4999 | ||||||
| Material | Stainless steel | ||||||
| Weight | 1kg | ||||||
| Thread Type | |||||||
| Metric 60° (20pc) | |||||||
| 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.75 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.5 |
| 1.75 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 |
| 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.0 | / | / | / | / |
| Metric 60° (24pc) | |||||||
| 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.35 | 0.4 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| 0.75 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.5 | 1.75 | 2.0 |
| 2.5 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 6.0 | / |
| Imperial 55° (28pc) | |||||||
| 4G | 4/2G | 5G | 6G | 7G | 8G | 9G | 10G |
| 11G | 12G | 13G | 14G | 16G | 18G | 19G | 20G |
| 22G | 24G | 25G | 26G | 28G | 30G | 32G | 36G |
| 40G | 48G | 60G | 62G | / | / | / | / |
| Imperial 55° (20pc) | |||||||
| 4 | 4.5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 22 |
| 24 | 28 | 40 | 48 | / | / | / | / |
| US 60° (30pc) | |||||||
| 4 | 4.5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 22 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 34 |
| 40 | 48 | 60 | 62 | / | / | / | / |
| US 60° (51pc) | |||||||
| 4 | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 |
| 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 30 | 34 |
| 36 | 38 | 40 | 42 | 44 | 46 | 48 | 50 |
| 52 | 54 | 56 | 58 | 60 | 62 | 64 | 66 |
| 68 | 70 | 72 | 74 | 76 | 78 | 80 | 82 |
| 84 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
Q1: What standards are used for thread gauges?
A1: Thread gauges are manufactured and calibrated according to various international and regional standards to ensure accurate and consistent measurements across applications. The most common standards include ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards for metric threads, ANSI/ASME (American National Standards Institute/American Society of Mechanical Engineers) standards for unified threads in the U.S., BS (British Standard) for British Standard Whitworth (BSW) and British Standard Pipe (BSP) threads, and DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) for German threads. Additionally, there are standards like JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) for Japanese thread specifications. These standards define parameters such as thread angle, pitch, and tolerances, ensuring compatibility and performance across diverse industries and applications.
Q2: How to know what size thread to use?
A2: To determine the correct thread size to use, you first need to identify key parameters of the threaded component: thread diameter, thread pitch (distance between threads), and thread type (metric, imperial, or another standard). Using a thread gauge is a simple way to measure these features, as it can help match the pitch and determine if the thread is coarse or fine. Additionally, consulting technical documentation, such as engineering drawings, standards tables, or specifications, can provide guidance on the appropriate thread size for a particular application. Consider factors like load-bearing capacity, material strength, and compatibility with mating parts to ensure the chosen thread size meets functional and safety requirements.
Q3: What is the difference between a thread pitch gauge and a thread gauge?
A3: A thread pitch gauge and a thread gauge serve distinct purposes in measuring and verifying threaded components. A thread pitch gauge is specifically used to measure the pitch or spacing between threads on a screw, bolt, or other threaded component. It helps identify the number of threads per inch (imperial) or the distance between threads (metric), making it useful for determining thread type and compatibility.
On the other hand, a thread gauge (also called a screw gauge) is used to verify the size, form, and accuracy of internal or external threads. It often includes go/no-go gauges that check if a threaded part meets dimensional tolerances and fits correctly. While the pitch gauge focuses on pitch measurement, the thread gauge is used to check overall thread quality and conformity.
Tips: How should thread gauges be maintained?
To maintain thread gauges in good working condition, it is crucial to keep them clean and free from debris, as dirt and contaminants can cause inaccurate readings or damage the gauge's precision surfaces.
Regularly wipe them down with a soft, lint-free cloth and apply a light coating of rust-preventive oil to protect against corrosion, especially if used in humid environments.
Store thread gauges in a dry place, ideally in protective cases, to prevent physical damage or deformation.
Handle them carefully to avoid dropping or knocking them against hard surfaces, as any dents or wear can affect accuracy.
Periodic calibration is also important to ensure the gauges meet specified tolerances, maintaining their reliability for precision measurements.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

