600W DC electronic load is designed specifically for CR-LED testing, enabling you to easily evaluate LED performance and ensure product quality and reliability. Whether you are a professional or an electronics enthusiast, this device provides unparalleled value at an economical price.
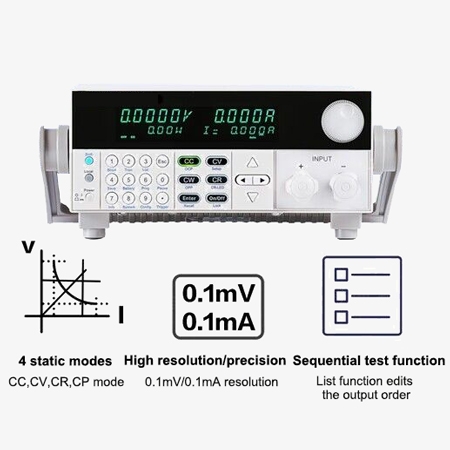
- 4 Operating Modes: The DC electronic load supports four modes: Constant Current (CC), Constant Voltage (CV), Constant Resistance (CR), and Constant Power (CP).
- Battery Discharge Testing: The programmable DC load tester includes a battery discharge testing feature with configurable termination conditions such as voltage, capacity, and time. During testing, users can monitor battery voltage, time elapsed, and discharged capacity.
- Advanced Control Software: The electronic load device is equipped with excellent control software for enhanced user experience and testing efficiency.
- Built-in Interfaces: SISCO adjustable electronic load includes built-in USB and RS232 interfaces for easy connectivity and communication.

- CR-LED Function Testing: This 600W programmable DC electronic load feature allows for real diode operation simulation, providing a more realistic representation of LED driver performance and simulating ripple current parameters during actual LED testing.
- Short Circuit Simulation: The 120V electronic load can simulate short circuit conditions at the input terminal for comprehensive testing.
- Automatic Testing: The programmable electronic load supports automatic testing functions for streamlined and efficient operations.
- Comprehensive Protection Features: This constant current electronic load includes over-voltage, over-current, over-power, over-temperature, and reverse polarity protection to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Applications
SISCO Electronic Loads are primarily used to test and evaluate power supply devices' performance and stability. They are widely used in power supply design, production testing, quality control, and research and development, simulating real load conditions to verify the reliability and efficiency of power products.

Production Test

R&D

Quality Control

Power Design
| Model | SISCO-IT8513C+ | ||
| Rating (0~40℃) | Input Voltage | 0~150V | |
| Input Current | 0~12A | 0~120A | |
| Input Power | 600W | ||
| Min. Operating Voltage | 0.2V/12A | 2V/120A | |
| Constant Voltage Mode | Range | 0.1~18V | 0.1~120V |
| Resolution | 1mV | 10mV | |
| Accuracy | ±(0.05%+0.02%FS) | ±(0.05%+0.025%FS) | |
| Constant Current Mode | Range | 0~12A | 0~120A |
| Resolution | 0.1mA | 1mA | |
| Accuracy | ±(0.05%+0.05%FS) | ||
| Constant Resistance Mode | Range | 0.05Ω~10Ω | 10Ω~7.5kΩ |
| Resolution | 16bit | ||
| Accuracy | 0.01%+0.08S*2 | 0.01%+0.0008S | |
| Constant Power Mode | Range | 600W | |
| Resolution | 10mW | ||
| Accuracy | ±(0.2%+0.2%FS) | ||
| Measuring Range | |||
| Voltage Readback Value | Range | 0~18V | 0~120V |
| Resolution | 0.1mV | 1mV | |
| Accuracy | ±(0.025%+0.025%FS) | ||
| Current Readback Value | Range | 0~12A | 0~120A |
| Resolution | 0.1mA | 1mA | |
| Accuracy | ±(0.05%+0.05%FS) | ||
| Power Readback Value | Range | 600W | |
| Resolution | 10mW | ||
| Accuracy | ±(0.2%+0.2%FS) | ||
| Protection Range | |||
| Over Power Protection | ≈620W | ||
| Over Current Protection | ≈13A | ≈130A | |
| Overvoltage Protection | ≈125V | ||
| Over Temperature Protection | ≈95℃ | ||
| Specifications | |||
| Short Circuit | Current (CC) | ≈13A/12A | ≈130A/120A |
| Voltage (CV) | 0V | ||
| Resistance (CR) | ≈15mΩ | ||
| Input Terminal Impedance | ≈150kΩ | ||
| Battery Test | Capacity | Max 999AH | |
| Dynamic Mode | Frequency | 0.1Hz~1kHz | |
| Dimensions | 214.5x88.2x453.5mm | ||
| Weight | 7.1kg | ||
Details
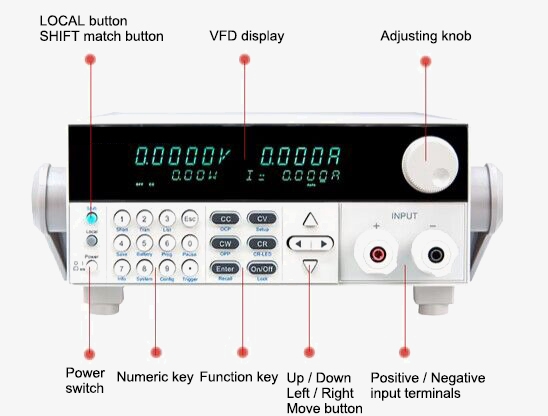

Q1: What is adjustable electronic load?
A1: An adjustable electronic load is a versatile testing device used to simulate various load conditions on power sources by allowing users to configure the load parameters to meet specific testing requirements. This flexibility makes it a valuable tool for evaluating the performance and reliability of power supplies, batteries, and other electronic devices.
Q2: How does an electronic load work?
A2: An electronic load works by simulating a real-world load on a power source, such as a battery or power supply, to test its performance and behavior under various conditions. It achieves this by dynamically adjusting its internal resistance to maintain a set current, voltage, resistance, or power level, depending on the selected operating mode (Constant Current, Constant Voltage, Constant Resistance, or Constant Power). The electronic load can accurately control and measure the input parameters, providing valuable data on the power source's capabilities, efficiency, and stability under different load scenarios.
Q3: What is an electronic load used for?
A3: An electronic load is used to test and evaluate the performance of power sources such as power supplies, batteries, and solar panels. It simulates various load conditions by drawing controlled amounts of current or power, allowing engineers to assess the reliability, efficiency, and behavior of the power source under different operating conditions. Electronic loads are essential in research and development, quality assurance, and production testing, helping ensure that power devices meet specified performance standards and can handle real-world usage scenarios.
Tips: What is regenerative electronic load?
A regenerative electronic load is a device that not only simulates electrical loads by drawing power from a source but also converts the absorbed power back into reusable electrical energy, typically feeding it back into the grid. This feature makes it energy-efficient and cost-effective for testing and evaluating power sources, such as batteries and power supplies, by reducing wasted energy during the testing process.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

