This is a portable 4-in-1 digital water quality tester that combines versatility, accuracy, and convenience. It is an indispensable tool for professionals and enthusiasts in fields such as agriculture, hydroponics, aquaculture, and water treatment.
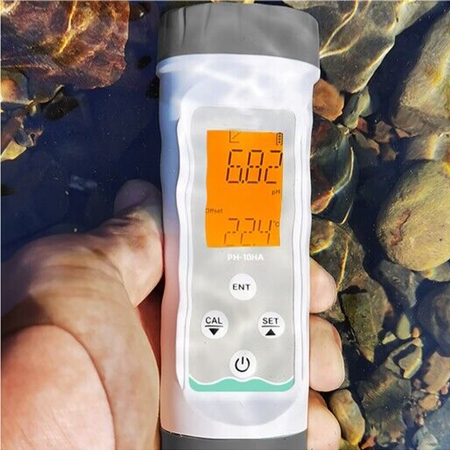

Multi-Functional Testing Modes
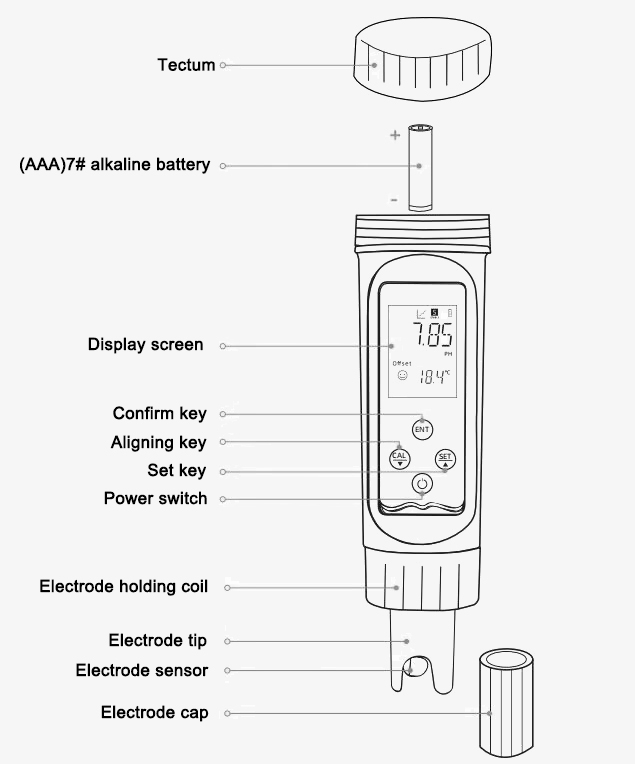
- IP67 protection rating ensures the digital water quality tester is protected against dust ingress and immersion in water up to a certain depth, making it suitable for use in various environments.
- Versatile handled water quality tester with multi-functional testing modes, easily switch between TDS, conductivity, salinity, and
measurement with the press of a button. - Utilizing NTC material, the external temperature sensor enhances response time and accuracy, guaranteeing a measurement precision of up to 0.1°C.
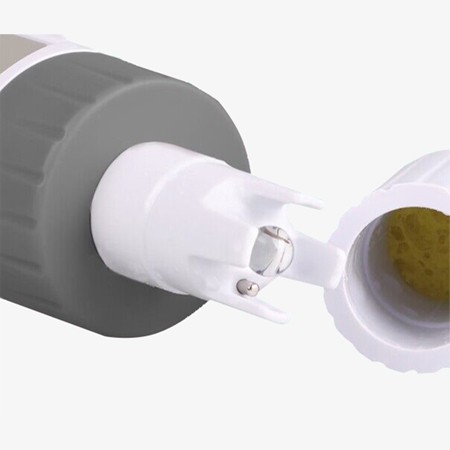

Efficient Power and Durability
- Powered by 7 AAA Alkaline batteries delivers sufficient power for prolonged operation, while the use of widely available AAA batteries ensures easy replacement and minimal downtime.
- Replaceable U-shaped glass electrode head for direct measurement without the need for soaking.
- Built to withstand the rigors of regular use, ensuring longevity and reliability in demanding laboratory or field settings.
- The handheld digital water quality tester incorporates a beeping function to signal various states, including powering on, completing calibration, achieving stable readings, and key presses.
Applications
SISCO's digital water quality tester offers high precision and versatility, delivering reliable solutions for water quality testing across diverse environments. From ensuring the safety of home drinkable water to managing and maintaining water quality in aquariums, this tester enables users to quickly and accurately measure key parameters like pH, TDS, salinity, temperature, and electrical conductivity (EC). It’s also ideal for testing well water to verify source safety and balancing pH in swimming pools to support a healthy swimming environment. Suitable for both home and commercial use, this tester meets a broad range of water quality testing needs.

Aquarium Water

Well Water

Tap Water

Drinking Water
| Model | SISCO-PM-DDS10 | |
| Basic Parameters | Electrode Sensor Type | U-shaped glass electrode |
| Calibration Method | Automatic, 1408μS/cm (1 point calibration) | |
| Display Mode | Rice digital screen | |
| Backlight Color | Orange | |
| Sound Switch | Yes | |
| Power Supply | (7#) AAA battery x 1PCS | |
| Weight | 650g | |
| Conductivity | Measuring range | 0.0μS/cm(ppm)- 20.00mS/cm(ppt) |
| Resolution | 0.1μS/cm(ppm)-0.01mS/cm(ppt) | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±1 %F.S | |
| Temperature | Measuring Range | 0.0-60°C/ 32-1 40°F |
| Resolution | 0.1°C | |
| Compensation Range | Automatic, 0-60°C/32-140°F | |
| Temperature Coefficient | 0.00-0.05, default 0.02 | |
| Reference Temperature Range | 10-40°C (default 25°C) | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±1%F.S | |
| Temperature Sensor Structure | External | |
| TDS | Measuring Range | 0-20.00ppt |
| TDS Coefficient | 0.01-1.0 adjustable (default 0.55) | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±1 %F.S | |
| Salinity | Measuring Range | 0-16.00ppt |
| Salinity Coefficient | NACL 0.65 | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±1%F.S | |
Details
Q1: What is a good TDS reading for drinking water?
A1: A good Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) reading for drinking water typically falls between 50 and 300 parts per million (ppm). Water with TDS levels within this range is generally considered safe and palatable, providing a balance of essential minerals without affecting taste or quality. While the World Health Organization (WHO) suggests that water with TDS levels below 300 ppm is acceptable, levels below 50 ppm may lack necessary minerals, and readings above 300 ppm can indicate excessive impurities or high mineral content, which could affect the taste and potentially pose health concerns over long-term consumption.
Q2: How do I use a water quality tester?
A2: Using a water quality tester is typically simple. For most handheld devices, you just need to dip the sensor or probe into the water, turn on the tester, and wait for the reading. Make sure to follow the SISCO's instructions for best results, as different testers may have specific setup requirements.
Q3: How to calibrate a 4 in 1 water quality tester?
A3: To calibrate the 4-in-1 digital water quality Tester, first, prepare the appropriate calibration solution. Turn on the device and immerse the probe in the solution. Press the calibration button and adjust the reading to match the solution’s standard value. After calibration, rinse the probe with distilled water and store it properly. Regular calibration ensures accurate and reliable measurements.
Tips: What parameters does the 4-in-1 Digital Water Quality Tester measure?
- Temperature – Displays the water temperature, which affects other water quality parameters like conductivity and salinity.
- Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) – Indicates the concentration of dissolved substances in water, helping assess water purity.
- Conductivity – Measures the water’s ability to conduct electricity, which reflects the level of dissolved ions.
- Salinity – Determines the salt concentration in water, useful for applications like aquaculture and marine environments.
This combination of measurements provides a comprehensive understanding of water quality for various applications, including drinking water, aquariums, hydroponics, and industrial water testing.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

