The leakage current tester is used to measure the leakage current, which is unrelated to the operation of the appliance, generated by the working power supply (or other power sources) through insulation or distributed parameter impedance. It serves as a testing and experimental device to assess the quality of the appliance's insulation and its overall safety performance.

Digital Display and Preset Functions Leakage Current Tester
- Digital display for test voltage, leakage current, and test duration: This allows for precise monitoring and ensures all test values are easy to read and track.
- Preset options for leakage current threshold and test time: Users can conveniently set specific parameters before starting the test, saving time and improving accuracy.

Alarm System and Flexible Control
- Sound and light alarms that activate when leakage current exceeds the set limit: The dual alarm system ensures that users are immediately alerted to any dangerous leakage currents, enhancing safety.
- Automatic or manual switching for test phase: This flexibility allows users to tailor the test process based on specific requirements, making it adaptable to different testing scenarios.
- Continuously adjustable settings for test time and alarm threshold: Fine-tuning these settings offers greater control over the test process, ensuring it meets precise testing standards.
Applications
The application field of the digital leakage current tester is extensive and includes various categories of electrical devices. It is suitable for household appliances such as TV sets, refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, dehumidifiers, electric blankets, and chargers. In the realm of instrumentation, it can be used with oscilloscopes, signal generators, DC power supplies, switching power supplies, and other complete machines. The tester is also applicable to lighting appliances, including ballasts, road lights, stage lights, portable lights, and other lamps. Furthermore, it is useful for electric heating appliances, such as electric drills, pistol drills, gas cutting machines, grinding machines, and electric welding machines. Finally, it can be employed with various motors, including rotating motors, ensuring safety and reliability across these diverse applications.
Instrumentation

Lighting Appliances

Electric Heating Appliances

Household Appliances
| Model | SISCO-LKT-2675WT |
| Output Voltage | 50~450V |
| Test Current | 0.2~2mA/2mA~20mA |
| Accuracy | ±5% |
| Testing Time | 0.1s~999s 0.0=continuous test |
| Transformer Capacity | Passive |
| PLC Interface | Optional |
| Power Requirements | 220V+10%, 50Hz±5% |
| Work Environment | 0-40°C, <85%RH |
| Dimensions (DxWxH) | 443x390x200mm |
| Weight | 10.5kg |
| Accessories | Power cord |
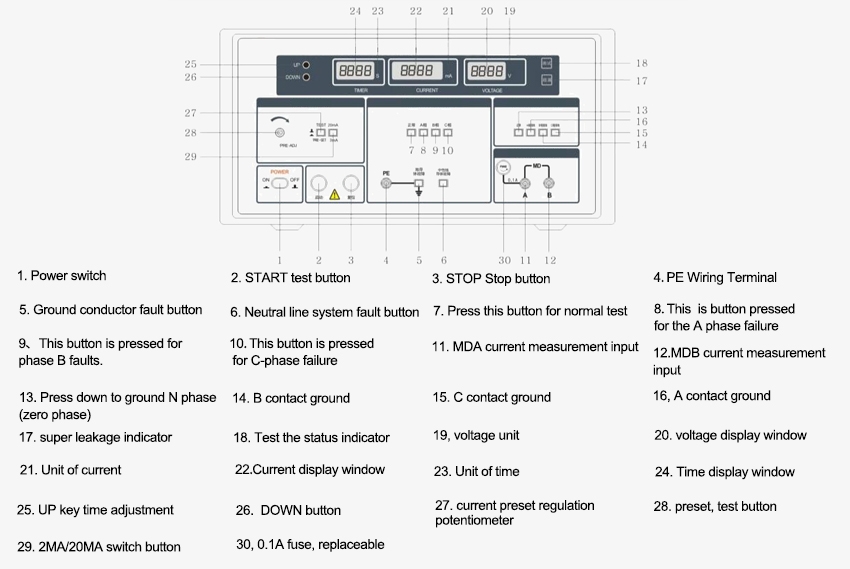
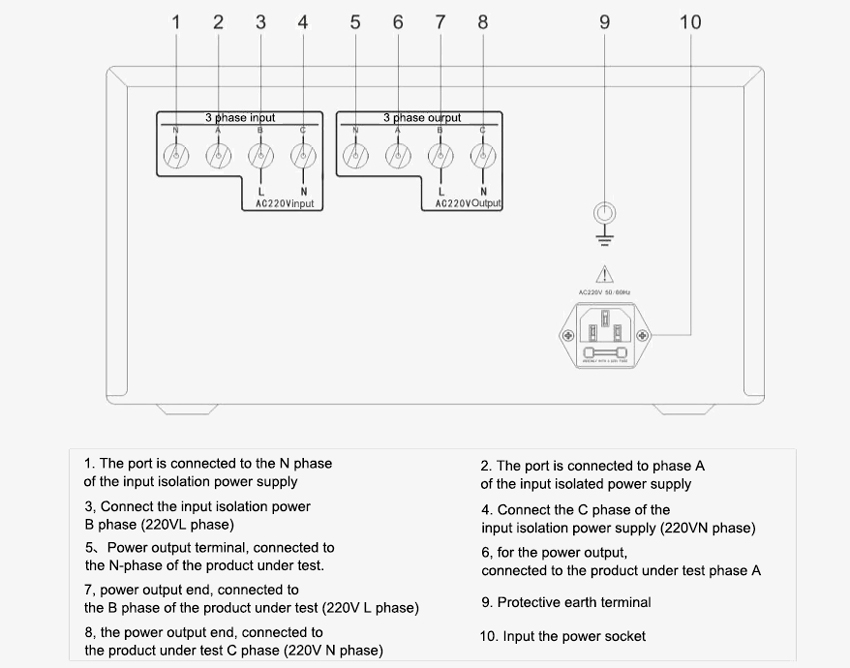
Details
Q1: What is a normal leakage current?
A1: Normal leakage current varies depending on the type of electrical equipment and its application, but generally, it should be minimal and within safe limits. For most household appliances, a leakage current of up to 0.5 mA is considered acceptable, while for medical devices, the limit can be as low as 10 µA. In industrial settings, the acceptable range can differ based on specific standards, but values typically range from 0.5 mA to 3.5 mA. Any leakage current significantly above these thresholds may indicate insulation failure or other electrical faults, posing safety risks and necessitating immediate inspection and remediation. Regular testing and monitoring are essential to ensure that leakage currents remain within safe limits to protect both equipment and users.
Q2: What are the types of leakage current?
A2: There are several types of leakage current that can occur in electrical systems, each arising from different causes and posing varying risks. Capacitive leakage current is caused by capacitive coupling between live conductors and nearby conductive surfaces, often seen in insulated cables and can increase with voltage. Conductive leakage current results from moisture, dust, or other contaminants that create a conductive path on the surface of insulation materials, leading to unintentional current flow. Inductive leakage current occurs due to electromagnetic induction, where nearby magnetic fields influence current flow in unconnected circuits. Ground leakage current refers to the current that flows through the ground conductor, often resulting from insulation breakdown or equipment faults. Understanding these types is crucial for implementing appropriate safety measures and ensuring the reliable operation of electrical equipment.
Q3: How to solve leakage current?
A3: To effectively solve leakage current issues, the first step is to conduct a thorough inspection and testing of the electrical system to identify the source of the leakage. This includes checking for damaged insulation, loose connections, and moisture ingress. Once identified, repair or replace faulty components such as cables, connectors, or insulation materials to eliminate the path for leakage current. Implementing proper grounding techniques can also help divert unwanted current safely away from equipment and users. Additionally, using residual current devices (RCDs) or ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) can provide added protection by quickly disconnecting the circuit when leakage current exceeds safe limits. Regular maintenance and monitoring through periodic testing can help prevent future leakage currents and ensure the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
Tips: How to maintain your digital leakage current analyzer?
- The leakage current test equipment should be used in a well-ventilated, dry environment free from dust and electromagnetic interference.
- If the tester is not used for an extended period, it should be powered on regularly, typically once a month, for at least 30 minutes.
- After prolonged operation, such as around 8 hours, the testing device should be turned off for more than 10 minutes to maintain its proper working condition.
- Over time, the leakage current tester may experience issues such as poor contact or disconnection, so regular maintenance is necessary.
Thank you for buying industrial test and measurement equipment on SISCO.com, all products sold by SISCO and the partner cover a 12 months warranty, effective from the date of receiving the products.
What is covered?
SISCO is responsible for providing free spare parts, and free technical support to assist the customer to repair the defective products until the problem is solved.
What is not covered?
- Product purchased from anyone other than a SISCO store or a SISCO authorized reseller.
- Expendable parts.
- Routine cleaning or normal cosmetic and mechanical wear.
- Damage from misuse, abuse or neglect.
- Damage from use of parts other than SISCO approved.
- Damage from use outside the product’s usage or storage parameters.
- Damage from use of parts not sold by SISCO.
- Damage from modification or incorporation into other products.
- Damage from repair or replacement of warranted parts by a service provider other than a SISCO authorized service provider.
- Damage caused by the application environment not meeting the product usage requirements and the failure to perform preventive maintenance.

